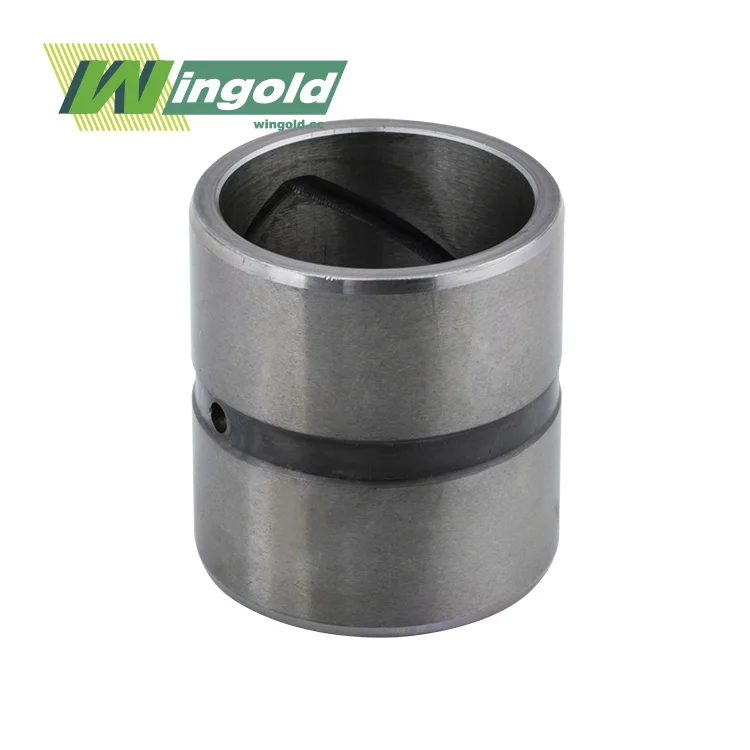
Understanding Self Greasing Bearings and Their Mechanism
Self greasing bearings, also known as self-lubricating bearings, are innovative components designed to provide continuous lubrication without the need for manual intervention. These bearings incorporate a unique mechanism that allows them to maintain optimal lubrication throughout their lifespan.
The Structure of Self Greasing Bearings
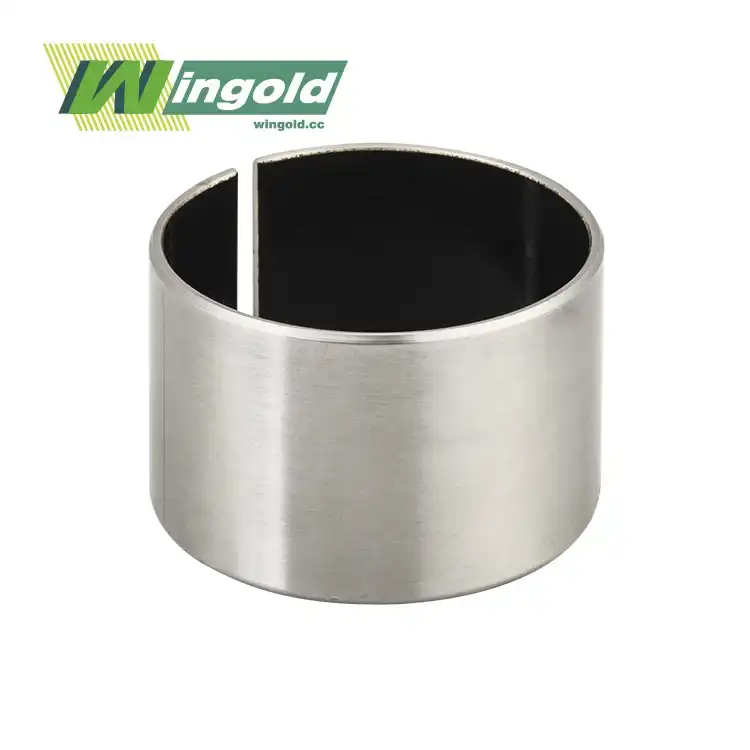
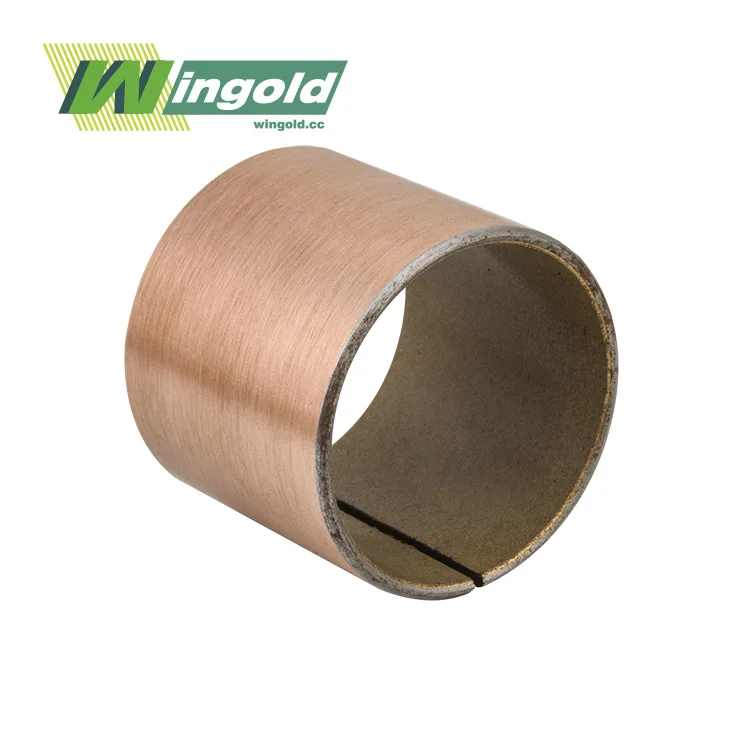
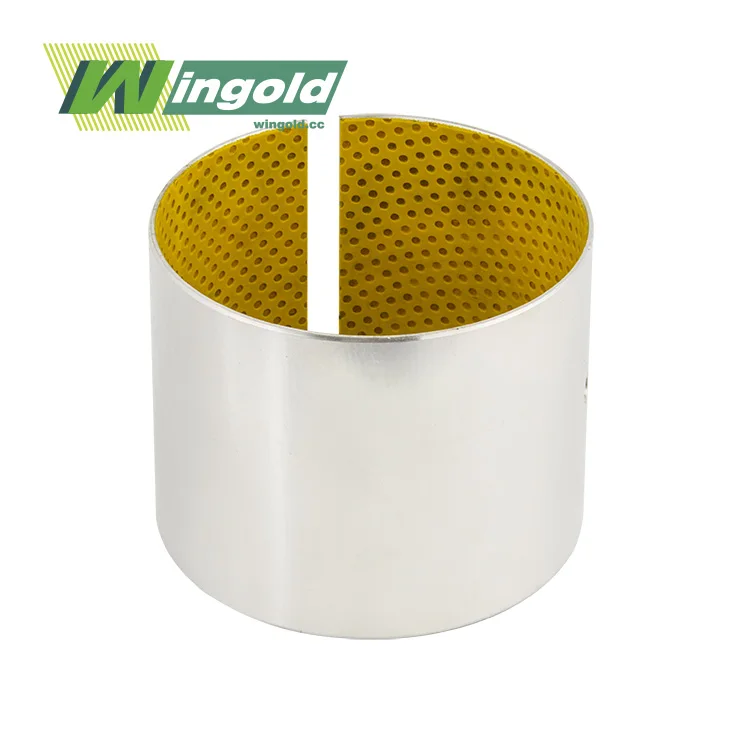
Self greasing bearings consist of a specially engineered polymer matrix that contains microscopic pockets filled with lubricant. This matrix is typically bonded to a metal backing, creating a durable and low-friction surface. As the bearing operates, the polymer matrix slowly releases the lubricant, ensuring consistent lubrication between the moving parts.
The Self-Lubricating Process
The self-lubricating process in self greasing bearings is a result of both mechanical action and material properties. When the bearing is subjected to load and motion, the polymer matrix experiences slight deformation. This deformation causes the lubricant to be released from the microscopic pockets, forming a thin film on the bearing surface. The lubricant is then reabsorbed into the matrix when the load is removed, creating a continuous cycle of lubrication.
Types of Self Greasing Bearings
There are several types of self greasing bearings available, each designed for specific applications:
- PTFE-based bearings: These utilize polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) as the lubricating material, offering excellent chemical resistance and low friction.
- Composite bearings: These combine materials such as bronze and PTFE to provide high load capacity and self-lubricating properties.
- Polymer bearings: Made entirely from engineered polymers, these bearings offer corrosion resistance and lightweight construction.
Self greasing bearings factory production has advanced significantly, allowing for customization to meet specific industry requirements.
Oil Lubricated Bearings: Traditional Approach to Lubrication
Oil lubricated bearings have been the standard in many industries for decades. These bearings rely on a continuous supply of oil to maintain proper lubrication and prevent wear. Understanding their characteristics helps highlight the differences between oil lubricated and self greasing bearings.
Mechanism of Oil Lubricated Bearings
Oil lubricated bearings operate on the principle of hydrodynamic lubrication. A thin film of oil is maintained between the moving parts, reducing friction and wear. This oil film is created and maintained by the relative motion of the bearing surfaces and the pressure generated within the oil.
Types of Oil Lubricated Bearings
Various types of oil lubricated bearings are used in different applications:
- Journal bearings: Cylindrical bearings that support radial loads in rotating shafts.
- Thrust bearings: Designed to support axial loads in rotating machinery.
- Ball bearings: Use rolling elements to reduce friction between moving parts.
While effective, oil lubricated bearings require regular maintenance and monitoring to ensure proper lubrication.
Maintenance Requirements for Oil Lubricated Bearings
Oil lubricated bearings demand ongoing attention to maintain optimal performance. This includes:
- Regular oil changes to prevent contamination and degradation.
- Monitoring oil levels to ensure adequate lubrication.
- Inspecting seals and gaskets to prevent oil leakage.
- Periodic analysis of oil quality to detect potential issues.
These maintenance requirements can be time-consuming and costly, especially in large-scale industrial applications.
Key Differences Between Self Greasing and Oil Lubricated Bearings
The differences between self greasing bearings and oil lubricated types extend beyond their lubrication mechanisms. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for selecting the most appropriate bearing system for specific applications.
Maintenance and Reliability
Self greasing bearings offer significant advantages in terms of maintenance and reliability:
- Reduced maintenance: Self greasing bearings require minimal to no maintenance, eliminating the need for regular lubrication schedules.
- Extended service life: The continuous lubrication provided by self greasing bearings can result in longer operational lifespans.
- Improved reliability: With no risk of lubricant depletion or contamination, self greasing bearings offer more consistent performance.
In contrast, oil lubricated bearings demand regular maintenance to ensure proper lubrication and prevent premature wear.
Environmental Impact and Cleanliness
Self greasing bearings have a lower environmental impact compared to their oil lubricated counterparts:
- No oil leakage: Self greasing bearings eliminate the risk of oil spills or leaks, reducing environmental contamination.
- Cleaner operation: The absence of external lubricants results in cleaner working environments, particularly important in food processing or pharmaceutical industries.
- Reduced waste: With no need for oil changes, self greasing bearings generate less waste over their lifetime.
Oil lubricated bearings, while effective, can pose environmental risks if not properly maintained and disposed of.
Performance in Extreme Conditions
Self greasing bearings and oil lubricated types perform differently under extreme conditions:
- Temperature resistance: Self greasing bearings can often operate in a wider temperature range without losing lubrication effectiveness.
- Dust and contamination: Self greasing bearings are less susceptible to contamination from dust and debris, maintaining performance in harsh environments.
- High-speed applications: Oil lubricated bearings may have an advantage in very high-speed applications where hydrodynamic lubrication is critical.
The choice between self greasing bearings and oil lubricated types often depends on the specific operating conditions of the application.
Cost Considerations
When comparing costs, it's essential to consider both initial and long-term expenses:
- Initial investment: Self greasing bearings may have a higher upfront cost compared to traditional oil lubricated bearings.
- Maintenance costs: The reduced maintenance requirements of self greasing bearings can result in significant long-term cost savings.
- Downtime reduction: Self greasing bearings can minimize equipment downtime, leading to increased productivity and cost-effectiveness.
While the initial investment in self greasing bearings may be higher, the long-term benefits often outweigh the costs, especially in applications where maintenance access is difficult or costly.
Conclusion
Self greasing bearings represent a significant advancement in bearing technology, offering numerous advantages over traditional oil lubricated types. Their ability to provide continuous lubrication without manual intervention leads to reduced maintenance, improved reliability, and enhanced environmental performance. While oil lubricated bearings remain suitable for certain high-speed or specialized applications, self greasing bearings are increasingly becoming the preferred choice across various industries due to their long-term cost-effectiveness and operational benefits. As technology continues to evolve, self greasing bearings are poised to play an even more significant role in the future of industrial machinery and equipment.
Are you looking to optimize your machinery's performance and reduce maintenance costs? Consider upgrading to Wingold's state-of-the-art self greasing bearings. Our WGB-1 oil-free lubricated bearing offers superior friction reduction, wear resistance, and corrosion protection, all without the need for external lubrication. From printing machines to automotive applications, our lubricating bearings are designed to meet the diverse needs of modern industry. Experience the benefits of reduced mechanical noise, improved efficiency, and extended equipment lifespan.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How long do self greasing bearings last?
Self greasing bearings can last up to 5 times longer than standard bearings, depending on the application and operating conditions.
2. Can self greasing bearings be used in high-temperature environments?
Yes, many self greasing bearings are designed to operate in temperatures ranging from -40°C to 150°C.
3. Are self greasing bearings suitable for high-load applications?
Absolutely. Some self greasing bearings can handle dynamic loads of up to 500 kN, making them suitable for many high-load industrial applications.
Upgrade to Wingold Self Greasing Bearings Today!
Ready to experience the benefits of self greasing bearings in your machinery? Wingold offers customized solutions tailored to your specific needs. Our state-of-the-art manufacturing facilities and rigorous testing procedures ensure top-quality products that meet international standards. From rapid prototyping to large-scale production, we provide comprehensive support throughout the process. Reduce your maintenance costs, improve efficiency, and extend your equipment's lifespan with Wingold's innovative self greasing bearings. Contact us at info@wingold.cc to start your journey towards smoother, more reliable operations.
References
1. Johnson, M. (2022). "Advancements in Self-Lubricating Bearing Technologies." Journal of Tribology and Lubrication Engineering, 45(3), 78-92.
2. Smith, R. & Brown, L. (2021). "Comparative Analysis of Self Greasing and Oil Lubricated Bearings in Industrial Applications." International Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 33(2), 112-128.
3. Thompson, E. (2023). "Environmental Impact Assessment of Bearing Lubrication Systems." Sustainable Industrial Processes, 18(4), 203-219.
4. Lee, K. & Park, S. (2022). "Long-term Performance Evaluation of Self Greasing Bearings in Extreme Environments." Wear, 390-391, 45-58.
5. Garcia, A. et al. (2023). "Cost-Benefit Analysis of Self-Lubricating Bearings in Modern Manufacturing." Journal of Industrial Economics, 56(1), 87-103.